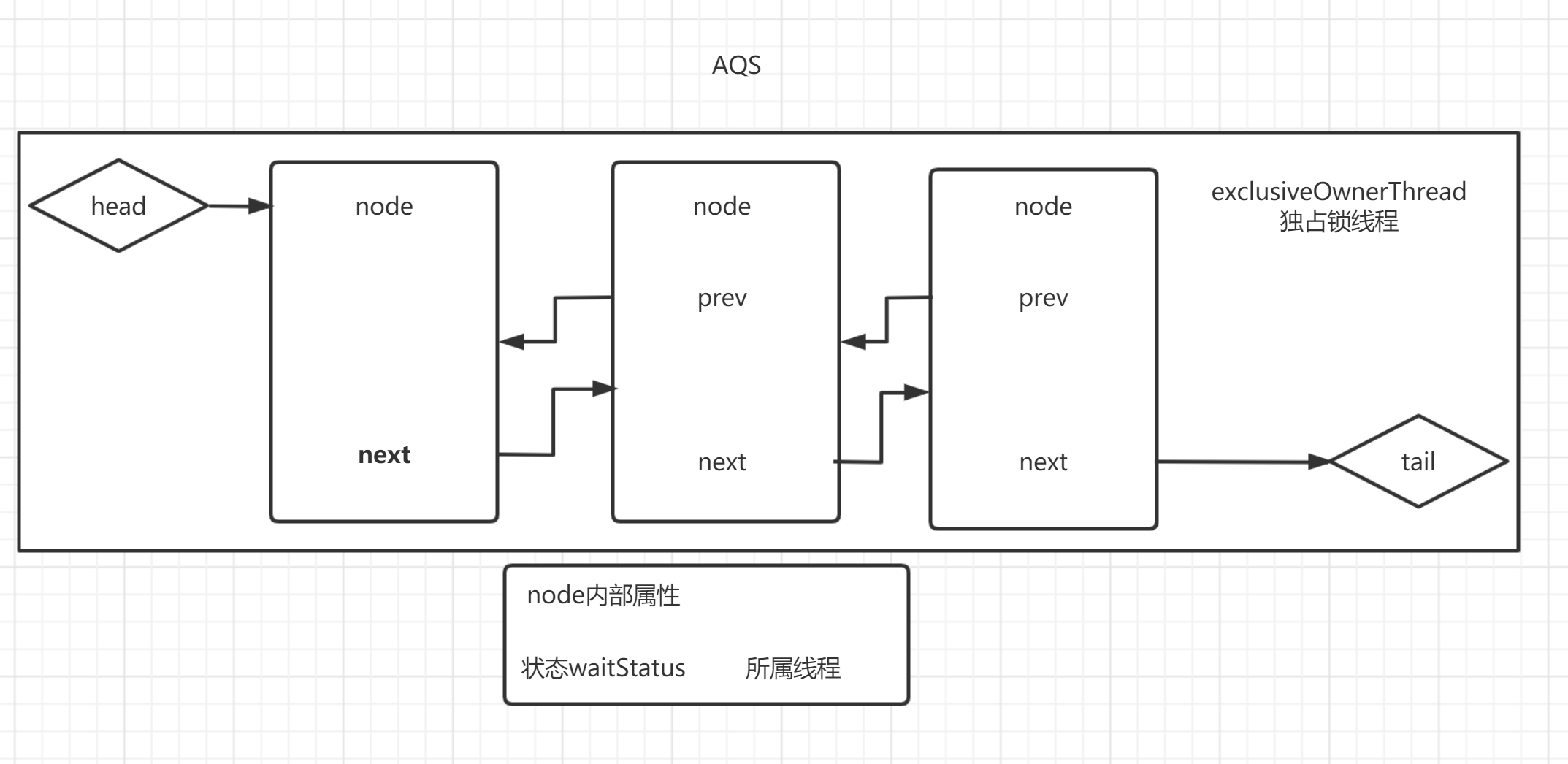
ReentrantLock 里面所使用到的基本结构
持有锁的waitstatus 状态 来标识node线程状态

重入是通过改变Lock本身的 state值值来说明线程的重入的。并且重入只改变了属性,并没有再次加锁。
线程的中断提醒**lock.lock()**情况下是不会提醒的 但是 此线程的 “打扰标志”会被设置, 可以通过isInterrupted()查看并 作出处理
lock是无法主动停止线程的,java也不推荐主动停止线程,一般都是通过中断标记,用户自己来处理线程后续的情况。
这也就是线程在被park阻塞 后被unpark唤醒时会返回线程的中断标记,到上层来通知调用者来处理线程的中断情况。
lock.lockInterruptibly() 会有提醒 并且会抛出异常来做中断处理;
非公平与公平的区别就在于非公平锁实现调用加锁时不是直接进入队列,而是先去cas一次尝试加锁。
并且在加锁前公平锁判断了当前node前面是否还有排队的node。而非公平锁没有判断,是直接通过cas尝试加锁。
cas 是更改的state值,通过偏移量寻找0去尝试更改为1 只有在第一次加锁会通过state的值做操作。
解锁就是唤醒下一个线程:先是改变state值 直到state=0才会执行unpark操作才会唤醒下一个线程,意味着lock与unlock需要成对出现。
代码分析–公平锁路线
加锁–lock
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 条件一:!tryAcquire 尝试获取锁 获取成功返回true 获取失败 返回false
// 条件一:如果是第一个线程 连node 都不会创建就直接加锁了
// 条件二.1 尝试添加进入AQS队列
// 条件二.2 acquireQueued 挂起当前线程 唤醒后相关的逻辑..
// acquireQueued 返回true 表示挂起过程中线程被中断唤醒过.. false 表示未被中断过..
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
|
尝试加锁–第一个线程加锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果当前状态是0 可以尝试加锁
if (c == 0) {
// 判断是否有前置node存在 有就返回true 说明当前线程只能入队
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
// 如果当前线程前面没得队列 那么可以尝试加锁 并且设置当前加锁线程给自己
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// 线程相等 说明重入
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
加锁失败–添加进入AQS队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程封装成node
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 尾巴结点拿出来赋值 据了解 别人这样写完全是更直观的看代码
Node pred = tail;
// 如果node已经存在就尝试加入尾结点后面
if (pred != null) {
// 设置当前节点上一个节点为 之前的尾结点
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
// 加入尾结点成功 设置之前尾结点的下一个几点为当前节点
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 1.当前队列是空队列 tail == null
// 2.CAS竞争入队失败..会来到这里..
enq(node);
return node;
}
// 自循环尝试加入队列
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
// 如果是空 队列 初始化一个node 为头
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 后面循环肯定会进入这里
node.prev = t;
// 尝试在尾巴节点加入自己 自循环知道成功为止
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
|
挂起线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
// 标识抢占锁是否成功
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 中断状态
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) { // 自循环
// 拿到上一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果上一个节点是头结点 说明有权利去抢占锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 加锁成功 设置自己为头结点
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 条件1 判断当前线程是否需要挂起
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// park 的时候会通过Thread.interrupted() 这个返回当前线程中断情况
// park 阻塞当前线程 如果中断 会返回interrupted以便selfInterrupt()这个方法使用,让外部线程知道中断状态
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
// 正常不会进来的 中断异常加锁方式 抛异常 会出来lockInterruptibly() 这个加锁方式
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 记住一点 外面是自循环 还会进来的 最终还是会执行到parkAndCheckInterrupt来park线程
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
// 拿到上一个节点的 状态 如果是signal=-1 说明 是一个持有锁的线程或者是一个可以唤醒下一个节点的线程
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
// 找到前置节点可以唤醒下一个节点的node 让他作为当前线程的前置节点
// 如果前置节点不是signal状态 那么当前线程将永远不会被唤醒
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
// 正常情况 进入这里
//当前node前置节点的状态就是 0 的这一种情况。
//将当前线程node的前置node,状态强制设置为 SIGNAl,表示前置节点释放锁之后需要 喊醒我..
// 这个 需要在释放锁成功后逻辑 看得出来
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
|
释放锁|唤醒后继节点–unlock
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public final boolean release(int arg) {
//尝试释放锁,tryRelease 返回true 表示当前线程已经完全释放锁
//返回false,说明当前线程尚未完全释放锁.. 解锁需要成对出现
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
//头结点
Node h = head;
//条件一:成立,说明队列中的head节点已经初始化过了,ReentrantLock 在使用期间 发生过 多线程竞争了...
// 只有在第二个线程进来时就会有head
//条件二:条件成立,说明当前head后面一定插入过node节点。节点去唤醒
// waitStatus 其他状态 后继节点在park前会改变前节点的值为-1 或者有其他状态
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
//唤醒后继节点..
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 状态-1
int c = getState() - releases;
// 异常情况
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
// 释放锁成功
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 如果是重复多次 将会返回false
setState(c);
return free;
}
// 唤醒后继节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
// 如果是小于0 说明下一个节点已经设置过你的值 直接开始修改值 这里对应shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 这个方法
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
Node s = node.next;
// 当前节点就是tail节点时 s == null
// 当新节点入队时 在并发情况下 s会可能有空的情况,因为添加队列是分三步执行的addWaiter(Node mode)方法
//当s.waitStatus>0 说明后继节点是取消状态,就要越过 那就要找其他节点来唤醒咯 配合cancelAcquire 异常退出时的取消状态判断
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
// 找到需要被唤醒的节点 从尾部开始
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
// 如果找到 就唤醒
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
|
加锁异常退出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
//因为已经取消排队了..所以node内部关联的当前线程,置为Null就好了。。
node.thread = null;
Node pred = node.prev;
// 如果前驱节点也是取消情况 找到第一个取消节点的node
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// 拿到取消节点的下一个节点
Node predNext = pred.next;
// 设置当前节点为取消节点
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
/**
* 当前取消排队的node所在 队列的位置不同,执行的出队策略是不一样的,一共分为三种情况:
* 1.当前node是队尾 tail -> node
* 2.当前node 不是 head.next 节点,也不是 tail
* 3.当前node 是 head.next节点。
*/
// 如果是尾结点 把队尾节点指向pred 不指向他自己了
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
// 然后在设置pred.nxet 指向null
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
int ws;
// 1.当前节点前驱节点不是head 那么他自己也就不是head.nxet
// 2. 前驱节点状态是 -1 或者0 或者 设置前驱节点 为-1 成功的话
// 设置成SIGNAL 状态后会唤醒后继节点 然后就会越过取消节点
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
// 修改前驱节点下一个指向 当前节点下一个节点存在的情况下并且状态不是取消状态
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
// 设置前驱节点的下一个节点为 当前node下个节点
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
// 如果是头结点的话直接唤醒下一个节点
// 后继节点唤醒后,会调用 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 会让node.next 节点越过取消状态的节点
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
// 自己指向自己 方便gc引用回收
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
|