基本结构图片
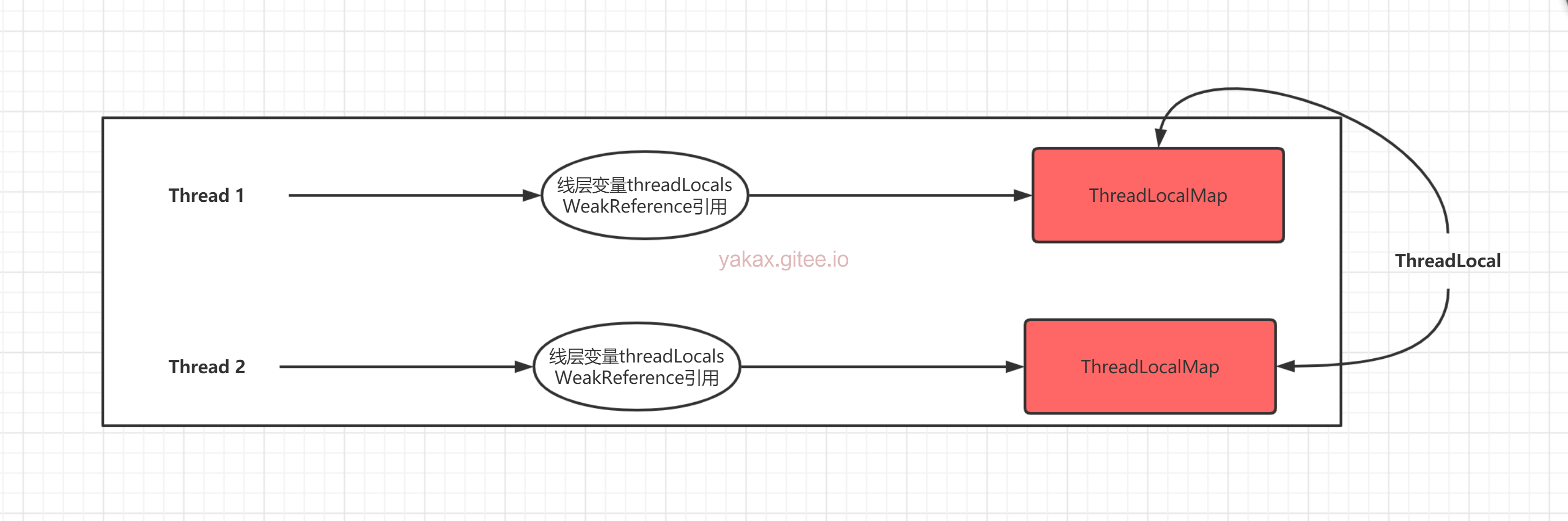
- 每个Thread 维护一个
ThreadLocalMap 映射表,这个映射表的 key 是 ThreadLocal实例本身,value 是真正需要存储的 Object所以ThreadLocal只有key的引用在 每个线程里面 - 也就是说
ThreadLocal 本身并不存储值,它只是作为一个 key 来让线程从 ThreadLocalMap 获取 value - 真正存数据的是Thread 的局部变量 threadLocals 的ThreadLocalMap里面的entry对象的value
OOM 问题
当ThreadLocal被回收 key的引用就消失了,key是弱引用,所以在gc时会被回收,但是里面的值一直绑定到线程本身没回收。如果使用的线程可以一直复用,那么数据就会一直在线程的threadLocals。所以在调用完要remove。
本身ThreadLocal也在规避这种问题,在做操作时都会利用线性探测、启发式清理,删除key为空的信息。
本身线程结束 其实也是能被回收的,主要是怕线程池,Thread.ThreadLocals会一直存在,占用内存,并且没有调用remove方法去规避。就是上图的连线没了 但是 线程一直没退出
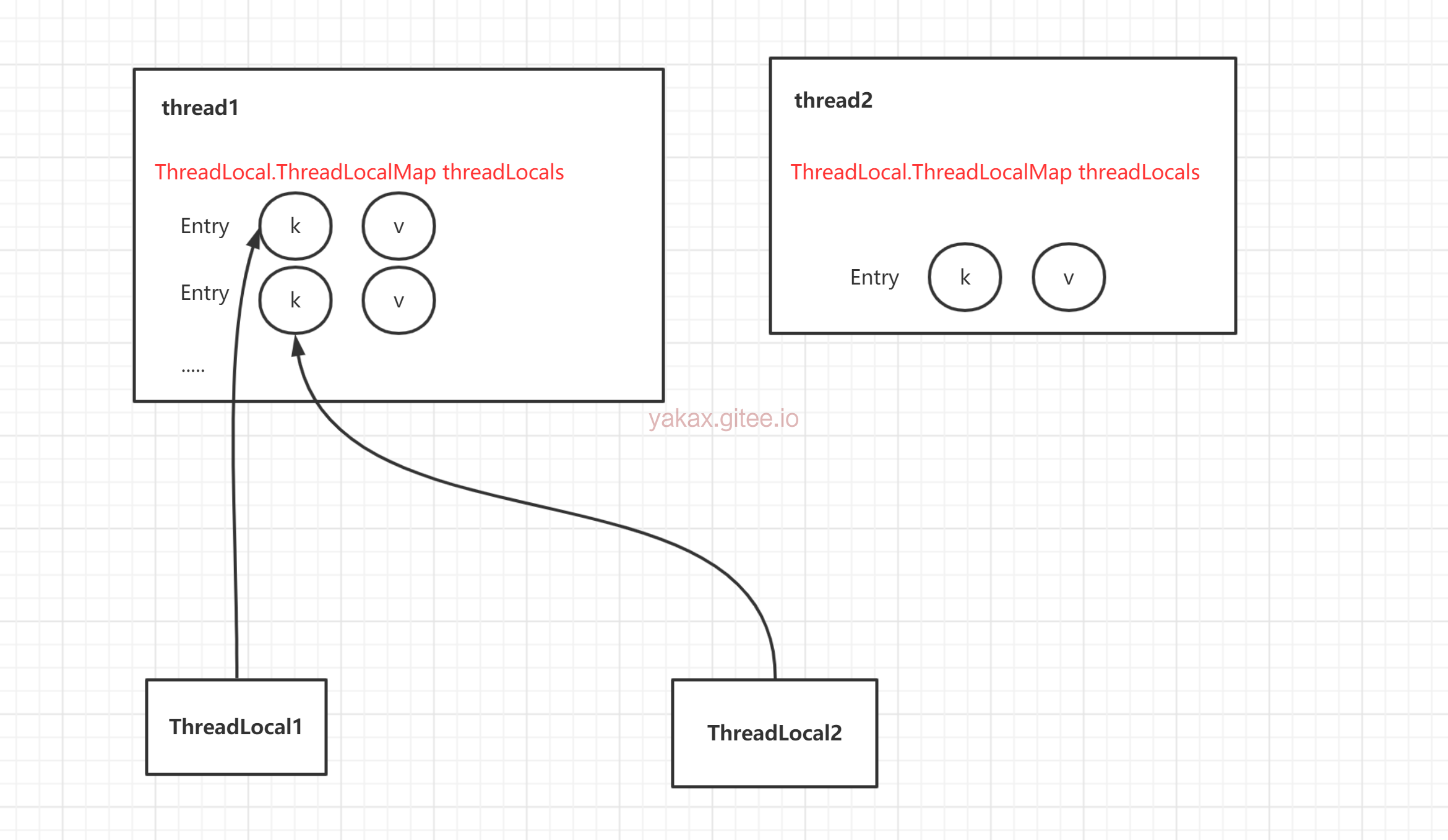
Thread Ref -> Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value
但是有一点要肯定的是,只要线程没退出,里面entry就有可能不会被回收,那么就可能造成泄漏。因为实际存储的数据不在threadLocal 而是在线程中。
源码分析
弱引用结构情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /**
* WeakReference 就跟没引用是类似的,如果发生垃圾回收,就会把这个对象回收掉。
* 当threadLocal对象失去强引用且对象GC回收后,
* 散列表中的与 threadLocal对象相关联的 entry#key 拿到的是null。
* 站在map角度就可以区分出哪些entry是过期的,哪些entry是非过期的。
* 我觉得 这样至少保证了ThreadLocal 不会内存泄漏
* entry里面的值通过调用set、get、remove的时候会被清除,会尽量删除 这样也会跟着线程的生命周期共存
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
|
set
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 是否存在关联的值
if (map != null)
// 替换
map.set(this, value);
else
// 创建
createMap(t, value);
}
|
set创建新值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
// 设置默认长度 16 entry
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// 通过 每个TheadLocal 独有的 nextHashCode 算出应该存放的位置
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
// 以每个TheadLocal为key 存放值为传进来的
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
// 长度1
size = 1;
// 设置扩容阈值
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
|
set替换值逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
// 拿到值 长度 算出 下标
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
// 向后查找
// 因为当前下标找不到 很可能是产生了 冲突了 会向后存放值
for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// key相等 替换
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
//条件成立:说明 向下寻找过程中 碰到key == null 的情况了,说明当前entry 引用没有了 是过期数据。
if (k == null) {
// 替换过期数据的逻辑。
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
//执行到这里,说明for循环碰到了 slot == null 的情况。
//在合适的slot中 创建一个新的entry对象。
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
// 增加size
int sz = ++size;
//做一次启发式清理
//条件一:!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) 成立,说明启发式清理工作 未清理到任何数据..
//条件二:sz >= threshold 成立,说明当前table内的entry已经达到扩容阈值了..会触发rehash操作。
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
|
set替换过期数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
// 传进来的 数据应该 放的下标
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
//条件成立:说明向前找到了过期数据,更新 探测清理过期数据的开始下标为 i
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
//以当前staleSlot向后去查找,直到碰到null为止。
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// key相同 替换操作
if (k == key) {
//替换值
e.value = value;
//交换位置的逻辑..
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists
// 如果之前的slotToExpunge 改变过 说明 当前下边前面出现过 过期数据
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
// expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge) 从过期数据开始 做一次探测式数据回收 传入下标
//cleanSomeSlots :启发式清理
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
//条件1:k == null 成立,说明当前遍历的entry是一个过期数据..
//条件2:slotToExpunge == staleSlot 成立,一开始时 的向前查找过期数据 并未找到过期的entry.
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
//因为向后查询过程中查找到一个过期数据了,更新slotToExpunge 为 当前位置。
//前提条件是 前驱扫描时 未发现 过期数据..
slotToExpunge = i;
}
//什么时候执行到这里呢?
//向后查找过程中 并未发现 k == key 的entry,说明当前set操作 是一个添加逻辑..
//直接将新数据添加到 table[staleSlot] 对应的slot中。
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them
// 如果向后查找发现有过期key 再次清理
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
|
set抹除过期数据段-探测式清理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| // 抹除过期数据段
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
// 拿到数据 和长度
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
// 使下标对应的value 为空 并且整个 entry 也为空
// help gc
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
// 元素个数-1
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
//for循环从 下标位置 + 1的位置开始搜索过期数据,直到碰到 Entry == null 结束。
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
// Entry 肯定不为空
// 返回 ThreadLocal key
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// 如果是过期数据 就置空 help gc
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
// 说明数据没过期 重新算位置
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
// 说明 下标位置不是最初算的位置,出现过冲突
if (h != i) {
//将entry当前位置 设置为null
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
//以正确位置 开始放,向后查找第一个 可以存放entry的位置。
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
// 返回最后null 的entry 的下标
return i;
}
|
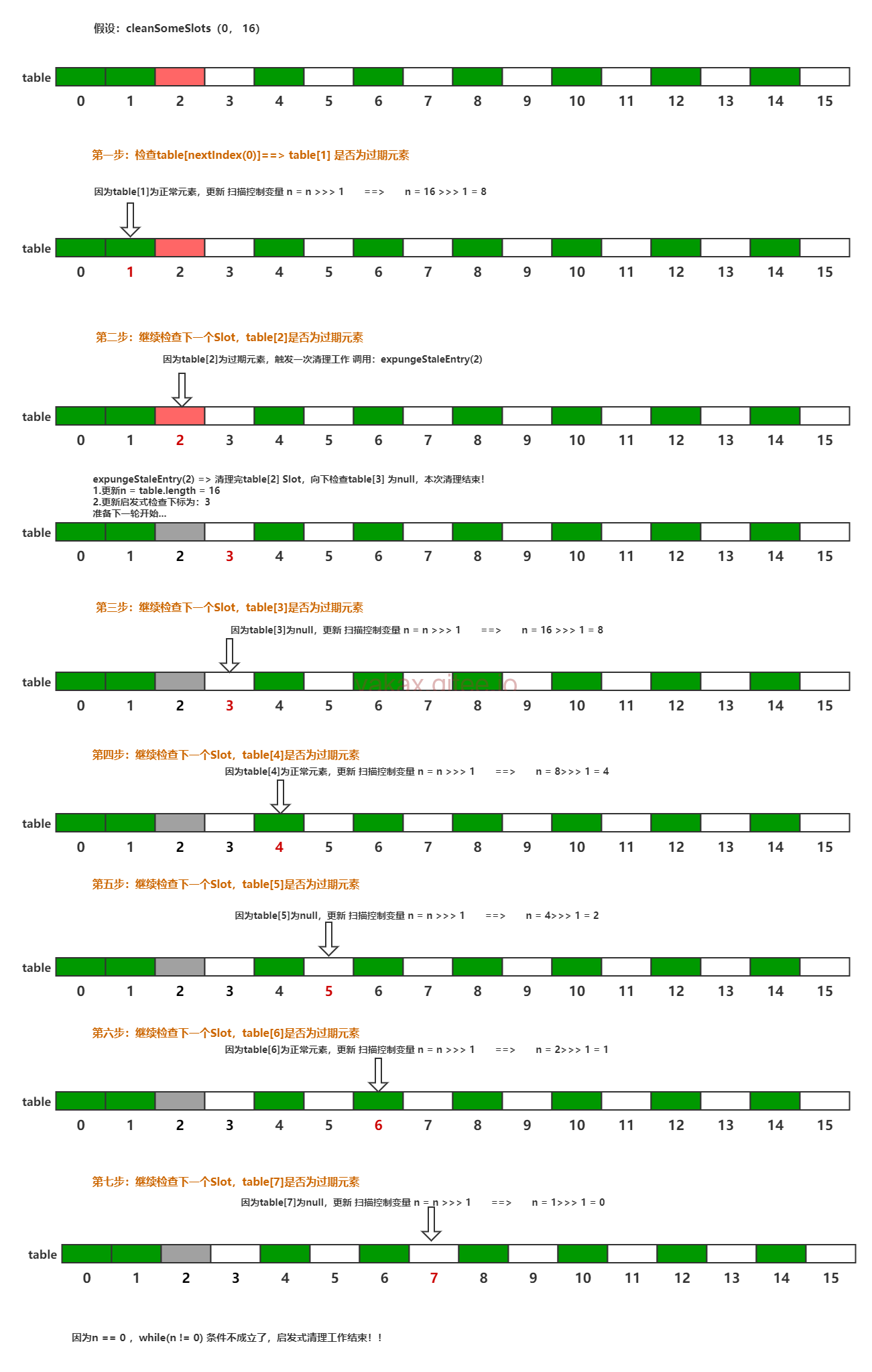
set启发式清理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| // 启发式清理
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
// i下标的值 肯定是null值 实际形成一个环绕式的访问。
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
// 如果entry不为空但是 key 为空 说明ThreadLocal被回收了
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
//重新更新n为 table数组长度
n = len;
// 标记被清理过
removed = true;
// 以当前下标为空开始 再次做探测式清理工作
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
// 假设table长度为16 目的还是为了 多做几次清理
// 16 >>> 1 ==> 8
// 8 >>> 1 ==> 4
// 4 >>> 1 ==> 2
// 2 >>> 1 ==> 1
// 1 >>> 1 ==> 0
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
|
get 与初始化ThreadLocalMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public T get() {
// 获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 根据线程去获取线程的ThreadLocalMap 局部变量
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
// 不等于null说明已经存在
// 获取当前ThreadLocal 关联当前线程 ThreadLocalMap.entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
// 存在就返回
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
// 有可能map未初始化 或者 map里面没有关联的值
// 初始化的工作 一般返回默认值
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
// 获取默认值 一般是null 重写过后自定义
// 类似 ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 99);
T value = initialValue();
// 获取当前线程 并拿到关联信息
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 通过当前线程 获取map
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 记住 这里的key 都是当前ThreadLocal 对象
if (map != null)
// 不等于null 就替换默认值
map.set(this, value);
else
// 转件新的ThreadLocalMap
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
|
get快速查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
// 根据 threadLocal 算出下标
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
// 拿到entry
Entry e = table[i];
// 如果值存在 并且 key相同则可以返回
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//有几种情况会执行到这里?
//1.e == null
//2.e.key != key
// 发生冲突 值会向后存放
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
|
get快速查询失败
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| /**
* @param key the thread local object threadLocal
* @param i the table index for key's hash code 下标
* @param e the entry at table[i] 下标对应的值
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 不等于null说明值存在 但是 key可能不同
while (e != null) {
// 拿到key
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
// key相同就返回
return e;
// 说明对应的threadLocal已经没了 因为key 是弱引用
if (k == null)
// 做一次探测式数据回收 传入下标 todo 这是在get数据时发现key为空的时候
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
// 出现冲突 向后查找并再次循环 查找值
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
// 未找到
return null;
}
|
resize()扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| private void resize() {
//获取当前散列表
Entry[] oldTab = table;
//获取当前散列表长度
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
//计算出扩容后的表大小 oldLen * 2
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
//创建一个新的散列表
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
//表示新table中的entry数量。
int count = 0;
//遍历老表 迁移数据到新表。
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
//访问老表的指定位置的slot
Entry e = oldTab[j];
//条件成立:说明老表中的指定位置 有数据
if (e != null) {
//获取entry#key
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//条件成立:说明老表中的当前位置的entry 是一个过期数据..
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
//执行到这里,说明老表的当前位置的元素是非过期数据 正常数据,需要迁移到扩容后的新表。。
//计算出当前entry在扩容后的新表的 存储位置。
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
//while循环 就是拿到一个距离h最近的一个可以使用的slot。
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
//将数据存放到 新表的 合适的slot中。
newTab[h] = e;
//数量+1
count++;
}
}
}
//设置下一次触发扩容的指标。
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
//将扩容后的新表 的引用保存到 threadLocalMap 对象的 table这里。。
table = newTab;
}
|
remove()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public void remove() {
//获取当前线程的 threadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
//条件成立:说明当前线程已经初始化过 threadLocalMap对象了
if (m != null)
//调用threadLocalMap.remove( key = 当前threadLocal)
m.remove(this);
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 算出 下标 查询到key相同 主动清理软引用
// 并执行一次 探测式清理
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
|




